
For example here a 6-bit pattern is replaced by 3 terms.

A string of n as is appended to the data unit. The various steps followed in the CRC method areġ.Appending the CRC to the end of the data unit should result in the bit sequence which is exactly divisible by the divisor. It should have exactly one less bit than divisor.Ģ. A sequence of redundant bits called CRC or CRC remainder is appended at the end of a data unit such as byte.Ī CRC will be valid if and only if it satisfies the following requirements:ġ. This technique is more powerful than the parity check and checksum error detection.If remainder after division is not zero, it indicates that the data unit has been damaged in transit and therefore it is rejected.If the remainder after division is zero then there is no error in the data unit & receiver accepts it.data + CRC is divided by the same number (predetermined binary divisor). At the destination, the incoming data unit i.e.The received frame is divided by P.īecause of no remainder, there are no errors. Suppose that there are no errors, and the receiver gets T perfect. The remainder is inserted to 2 5D to provide T = 101000110101110 that is sent. The message is generated through 2 5:accommodating 1010001101000 The CRC of n bits interpreted in phase 2 restores the added 0s at the end of the data unit. The new data unit is divided by a divisor utilizing a procedure known as binary division the remainder appearing from the division is CRC. The number n is one smaller than the number of bits in the fixed divisor. Joining it to the end of the data unit should create the resulting bit sequence precisely divisible by the divisor.Ī string of n 0s is added to the data unit.
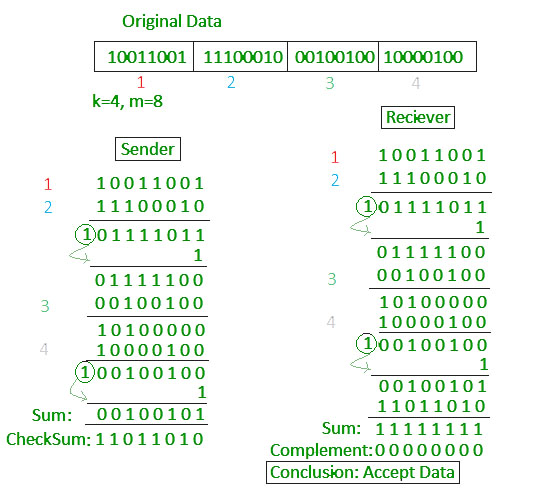
It should have accurately one less bit than the divisor. The redundancy bits used by CRC are changed by splitting the data unit by a fixed divisor. Modulo 2 Arithmetic is used in this binary addition with no carries, just like the XOR operation. The out coming frame, including n bits, is precisely divisible by some fixed number. It is given as a kbit message and the transmitter creates an (n – k) bit sequence called frame check sequence. The Cyclic Redundancy Checks (CRC) is the most powerful method for Error-Detection and Correction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
